Today the topic is a compound related to DMT, called dipropyltrytamine (DPT). It is also a psychoactive drug belonging to the tryptamine family. Naturally it does not occur but ofcourse in the labratorium it is synthesized.
Although it is chemically similiar to dimethyltryptamine, its psychoactive effects are very different. The most prominent effects are increased intensity of music, colours. A pleasant sensation of warmth and the death of the ego. While experiencing the presence of other beings as with DMT the perspective is more as an observer or a watcher opposed to DMT which the person may feel being in contact with the entitiy. The loss of the ego boundary is also reported when a person has trouble distinguishing the boundary between him/herself and other objects and reality its self. Sensory input may also become blended; this is a distinct from synaesthesia
A user may also encounter abnormal feelings experiencing them simultaneously. One may have the experience of seeing the universe from different locations in space and time. Visual hallucinations are often geometric and spiraled. Other hallucinations tend to be experienced in the peripheral vision. Not very much is known about the brotherly compound of DMT but users do report these effects when the drug is taken. If you have any experiences related to DPT please do post them and share your experiences.
maandag 29 oktober 2012
dinsdag 23 oktober 2012
Dimethyltryptamine
So now we're going to entertain ourselves with the fascinating organic molcule: DMT, or dimethyltryptamine. (N,N-DMT)
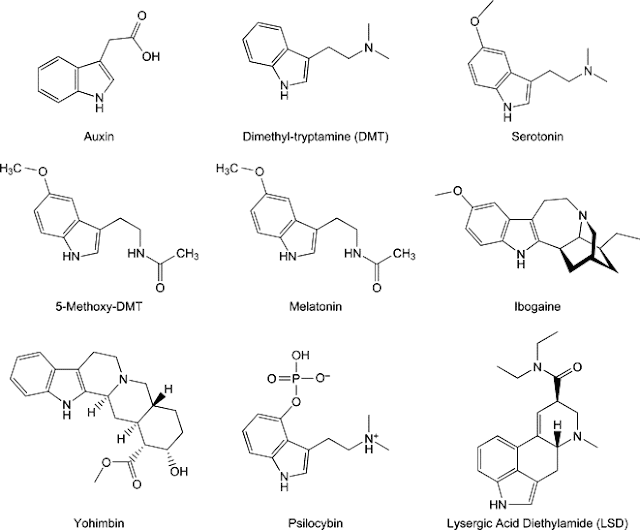
DMT is a naturally occuring psychedelic compound of the tryptamine family. Its presence is widespread throughout the plant kingdom. It also occurs in traces (trace amine) in mammals, primarily pointing at the direction of humans. It functions as a trace amine neurotransmitter derived from the essential amino acid tryptophan, which is found in high concentrations in chocolate, oats, milk, cheese, red meat, eggs, poultry, fish, and other protein-based foods. Through the help of the enzyme INMT tryptophan is synthesized into DMT during normal metabolism. Structurally DMT is analogous to the neurotransmitter serotonin, melatonin and other psychedelic tryptamines.
When ingested orally DMT acts as a psychedelic drug but its effects depend purely on the dose and method of administration. As the bodies MAO enzymes break it down almost instantly. For this reason when ingested orally MAOI inhibitors is usually also ingested, to prolong the effect. The effects of DMT can range from mild psychedelic states to powerful out of this world experiences as reported by users and clinical trials. These experiences are often described as a total loss of connection to the conventional reality and the encounter of different dimensions. More on this subject can be found in Dr. Strassman's book: DMT the spirit molecule.
What scientists have not figured out is what mechanism causes these strange hallucinations and out of this wordly connections to these other dimensions as described by the volunteers and users of DMT.
More on this subject in future topics, If you have any experience with DMT please feel free to share it.
DMT is a naturally occuring psychedelic compound of the tryptamine family. Its presence is widespread throughout the plant kingdom. It also occurs in traces (trace amine) in mammals, primarily pointing at the direction of humans. It functions as a trace amine neurotransmitter derived from the essential amino acid tryptophan, which is found in high concentrations in chocolate, oats, milk, cheese, red meat, eggs, poultry, fish, and other protein-based foods. Through the help of the enzyme INMT tryptophan is synthesized into DMT during normal metabolism. Structurally DMT is analogous to the neurotransmitter serotonin, melatonin and other psychedelic tryptamines.
When ingested orally DMT acts as a psychedelic drug but its effects depend purely on the dose and method of administration. As the bodies MAO enzymes break it down almost instantly. For this reason when ingested orally MAOI inhibitors is usually also ingested, to prolong the effect. The effects of DMT can range from mild psychedelic states to powerful out of this world experiences as reported by users and clinical trials. These experiences are often described as a total loss of connection to the conventional reality and the encounter of different dimensions. More on this subject can be found in Dr. Strassman's book: DMT the spirit molecule.
What scientists have not figured out is what mechanism causes these strange hallucinations and out of this wordly connections to these other dimensions as described by the volunteers and users of DMT.
More on this subject in future topics, If you have any experience with DMT please feel free to share it.
Trace Amines
It's been a while since my last update it has been a busy time for me but now I'm back and hopefully updates every couple of days. The subject today is trace amines, what they are, how they work and what roll they play in our body.
Trace amines are a group of amines (found in the human body) structurally related to monoamine neurotransmitters such as we all know; dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin. Compared to these monoamines, trace amines are present in trace concentrations. They are distributed throughout our brain and peripheral nervous tissues and break down faster than classical neurotransmitters. Trace amines may play very significant roles in the coordination of monoamine-based synaptic physiology at high concentrations for example they have amphetamine-like effects on monoamine release, reuptake and biosynthesis of the classic neurotransmitters. At lower concentrations they possess postsynaptic effects that potentiate the effects of other neurotransmitters; particularly dopamine and serotonin.
A family of G protein couple receptors has been characterized to be responsive to trace amines. And structurally related to psychoactive drugs such as amphetamine, 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methylamphetamine, lysergic acid diethylamide and dimethyltryptamine. Like dopamine, noradrenaline, and serotonin the trace amines have been implicated in a variety of human disorders of affect and cognition such as depression and schizophrenia. How these endeogenic amines are related to psychoactive molecules found in nature is still a mystery scientists are trying to solve. Why do molecules in our brain found in trace amounts look so much alike structurally and chemically to psychoactive drugs found in nature?
Trace amines are a group of amines (found in the human body) structurally related to monoamine neurotransmitters such as we all know; dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin. Compared to these monoamines, trace amines are present in trace concentrations. They are distributed throughout our brain and peripheral nervous tissues and break down faster than classical neurotransmitters. Trace amines may play very significant roles in the coordination of monoamine-based synaptic physiology at high concentrations for example they have amphetamine-like effects on monoamine release, reuptake and biosynthesis of the classic neurotransmitters. At lower concentrations they possess postsynaptic effects that potentiate the effects of other neurotransmitters; particularly dopamine and serotonin.
A family of G protein couple receptors has been characterized to be responsive to trace amines. And structurally related to psychoactive drugs such as amphetamine, 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methylamphetamine, lysergic acid diethylamide and dimethyltryptamine. Like dopamine, noradrenaline, and serotonin the trace amines have been implicated in a variety of human disorders of affect and cognition such as depression and schizophrenia. How these endeogenic amines are related to psychoactive molecules found in nature is still a mystery scientists are trying to solve. Why do molecules in our brain found in trace amounts look so much alike structurally and chemically to psychoactive drugs found in nature?
zondag 15 juli 2012
Mimosa Hostilla
Welcome to my freshly made blog!
I made this blog to share my knowledge and information I have gathered about psychoactive substances and the interesting history they have with mankind.. If you are interested in learning more about the wonderful world of the mushrooms and the many different psychoactive plants that exist in nature and the biochemical pathway they follow, the effect they have on the human brain you will find this blog helpful. Note though I do not recommend nor promote the use of substances that are illegal by law in your state or country. This blog is meant to inform you on the subject and nothing more.
I will update the blog multiple times a week and post about a specific plant or other hallucogenic. We're going to start off this week with Mimosa Hostilla. If you have any questions or recommendations on what to write about please let me know. I have acces to a library full of information and I would love to share it with other people who share this hobby.
Mimosa Hostilla
I made this blog to share my knowledge and information I have gathered about psychoactive substances and the interesting history they have with mankind.. If you are interested in learning more about the wonderful world of the mushrooms and the many different psychoactive plants that exist in nature and the biochemical pathway they follow, the effect they have on the human brain you will find this blog helpful. Note though I do not recommend nor promote the use of substances that are illegal by law in your state or country. This blog is meant to inform you on the subject and nothing more.
I will update the blog multiple times a week and post about a specific plant or other hallucogenic. We're going to start off this week with Mimosa Hostilla. If you have any questions or recommendations on what to write about please let me know. I have acces to a library full of information and I would love to share it with other people who share this hobby.
Mimosa Hostilla
BOTANICAL CLASSIFICATION
Family : Fabaceae
Genus :Mimosa
Species :tenuiflora
Mimosa hostilla, is a evergreen tree or shrub native to the northeastern region of Brazil and found as far north as southern Mexico. It is most often found in lower altitudes, but it can be found as high as 1 km.
The Mayans of Mexico have used Mimosa Hostilla bark to treat lesions of the skin for over a thousand years.
Powdered Mimosa Hostilla bark contains large amounts (16%) of biomolecules , which act as an astringent making the skin stop bleeding. This helps protect the body from infection, while the skin builds new protective tissue.
Biomolecules in the bark diminish capillary permeability.It contains antioxidant flavonoids.
It is now used in commercial hair and skin products that claim to rejuvenate skin. The bark is known to be rich in many different organic molecules that seem to have a beneficial effect on the skin and hair.
Mimosa Hostilla is an entheogen known as Jurema. Mimosa hostilla root bark has been recently shown to have a Dimethyltryptamine content of about 1%. The stem bark has about 0.03% DMT. The bark is the part of the tree traditionally used in Brazil in a brew also called Jurema or Yurema. At the same time the traditional Western Amazonian sacrament Ayahuasca is brewed from indigenous ayahuasca vines.
Mimosa Hostilla is different when it comes to the pharmacological understanding of how DMT from the plant is rendered orally active as an entheogen.. If MAOI is neither present in the plant nor added to the mixture, the enzyme MAO will break apart DMT in the human gut, preventing the active molecule from entering the blood stream leading to the brain. This means if the brew is consumed consisting of only Mimosa Hostilla rootbark it should not be active but it is. This question still has to be answered but some studies have shown progress into this mystery.
source:
The Encyclopedia of Psychoactive Plants: Ethnopharmacology and Its Applications
Biomolecules in the bark diminish capillary permeability.It contains antioxidant flavonoids.
It is now used in commercial hair and skin products that claim to rejuvenate skin. The bark is known to be rich in many different organic molecules that seem to have a beneficial effect on the skin and hair.
Mimosa Hostilla is an entheogen known as Jurema. Mimosa hostilla root bark has been recently shown to have a Dimethyltryptamine content of about 1%. The stem bark has about 0.03% DMT. The bark is the part of the tree traditionally used in Brazil in a brew also called Jurema or Yurema. At the same time the traditional Western Amazonian sacrament Ayahuasca is brewed from indigenous ayahuasca vines.
Mimosa Hostilla is different when it comes to the pharmacological understanding of how DMT from the plant is rendered orally active as an entheogen.. If MAOI is neither present in the plant nor added to the mixture, the enzyme MAO will break apart DMT in the human gut, preventing the active molecule from entering the blood stream leading to the brain. This means if the brew is consumed consisting of only Mimosa Hostilla rootbark it should not be active but it is. This question still has to be answered but some studies have shown progress into this mystery.
source:
The Encyclopedia of Psychoactive Plants: Ethnopharmacology and Its Applications
Christian Ratsch (Author), Albert Hofmann (Foreward) (Author)
Abonneren op:
Reacties (Atom)

 \
\